The Definitive Guide to Choosing the Right CPAP Machines
What Are CPAP Machines and How Do They Treat Obstructive Sleep Apnoea?
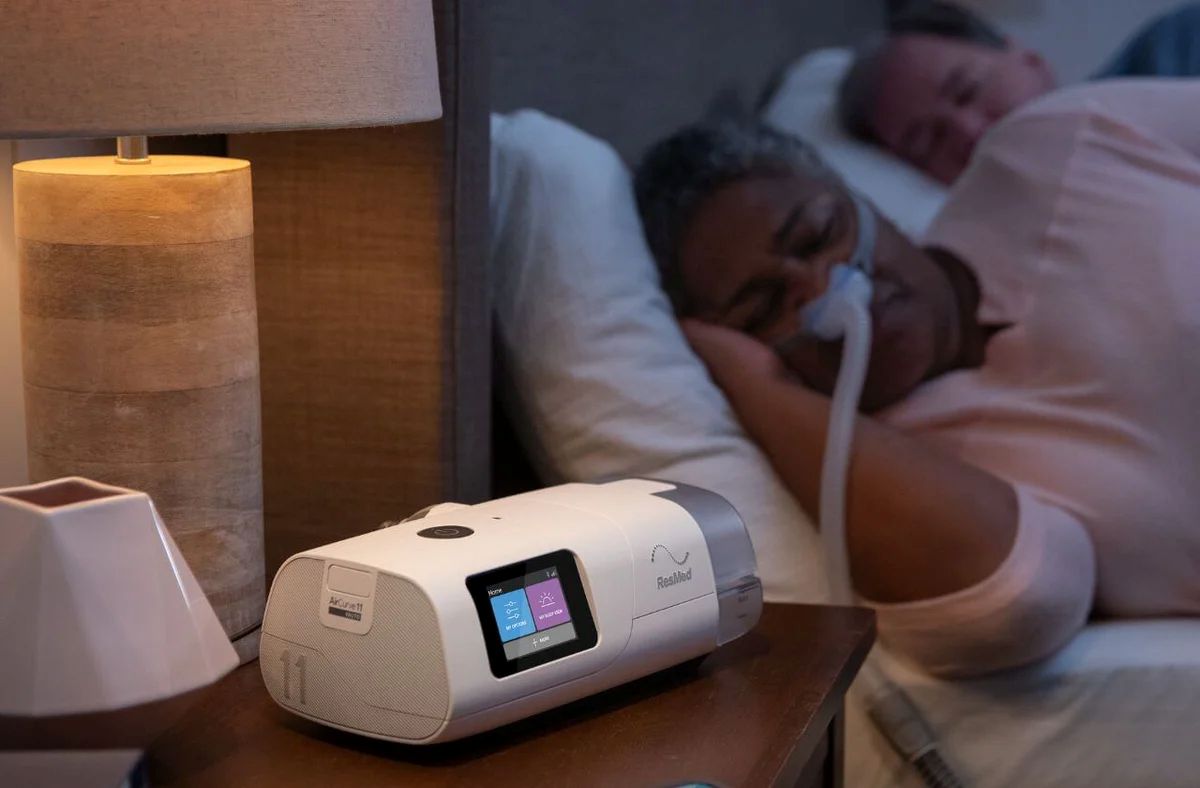
CPAP machines deliver a continuous stream of pressurised air through a mask worn during sleep, keeping your airways open and preventing the breathing interruptions characteristic of obstructive sleep apnoea. The device consists of three main components: a motor that pressurises room air, a hose that transports the air, and a mask that delivers it directly to your airways.
When you have OSA, the soft tissues in your throat relax and collapse during sleep, blocking your airway. This causes repeated breathing pauses that can occur dozens or even hundreds of times per night. CPAP therapy acts as a pneumatic splint, using gentle air pressure to hold these tissues in place and maintain an open passage for breathing.
The pressurised air creates positive pressure in your upper airway, preventing the collapse that triggers apnoea events. This allows you to breathe normally throughout the night, maintaining proper oxygen levels in your blood and preventing the frequent awakenings that fragment your sleep.
Selecting the right CPAP machine directly impacts your treatment success. A poorly chosen device can lead to discomfort, poor sleep quality, and ultimately, abandonment of therapy. Studies show that patient adherence to CPAP therapy depends heavily on comfort factors, ease of use, and how well the machine fits into your lifestyle.
The ideal CPAP machine balances therapeutic effectiveness with personal comfort preferences. Features like quiet operation, intuitive controls, and appropriate pressure settings make the difference between a device you’ll use consistently and one that ends up gathering dust. Your choice should account for your specific sleep patterns, breathing needs, and lifestyle requirements to ensure you receive the full benefits of treatment.
What Are the Different Types of CPAP Machines?
CPAP machines fall into two primary categories: fixed pressure devices and auto-adjusting models. Understanding the differences between these types helps users select equipment that matches their specific sleep apnoea patterns and lifestyle requirements.
Fixed Pressure CPAP
Fixed pressure CPAP machines deliver a single, predetermined air pressure throughout the entire night. A sleep specialist determines this pressure setting during a titration study, where they monitor your breathing patterns and adjust the pressure until they find the optimal level to keep your airway open. Once set, the machine maintains this exact pressure from the moment you switch it on until you wake.
These devices offer straightforward operation with minimal complexity. The consistent pressure delivery makes them reliable for individuals whose sleep apnoea severity remains stable throughout the night. Fixed pressure machines typically cost less than their auto-adjusting counterparts, making them an economical choice for budget-conscious users.
The main limitation lies in their inflexibility. Your breathing needs may change based on sleep position, sleep stage, or even seasonal factors like allergies. A fixed pressure cannot adapt to these variations, potentially delivering more pressure than needed during certain periods or insufficient pressure during others.
Auto-Adjusting CPAP Machines
Auto-adjusting CPAP machines, often called AutoSet devices, use sophisticated algorithms to monitor your breathing patterns in real time. These machines detect changes in airflow resistance, apnoea events, and breathing effort, then automatically adjust the pressure within a prescribed range to deliver exactly what you need at any given moment.
The technology responds to various factors affecting your breathing:
- Sleep position changes: Higher pressure when lying on your back, lower when side-sleeping
- Sleep stage transitions: Different pressure requirements during REM versus non-REM sleep
- Nasal congestion: Increased pressure to compensate for restricted nasal passages
- Weight fluctuations: Adjusted pressure as body composition changes
Auto-adjusting machines provide several advantages. They often improve comfort by reducing unnecessary pressure exposure, which can decrease side effects like aerophagia (air swallowing) or mask leaks. Many users find them easier to tolerate during the adaptation period since the pressure starts low and increases only as needed.
These devices also generate detailed data about your nightly.
Which Comfort Features Should Users Look For in a CPAP Machine?
Comfort features directly determine whether users will consistently use their CPAP therapy each night. The most critical features include humidification, heated tubing, ramp functionality, and quiet operation—each addressing specific challenges that can otherwise derail treatment adherence.
Why Humidification Matters for CPAP Therapy
Built-in humidifiers combat one of the most common complaints among CPAP users: dry, irritated airways. The constant stream of pressurised air naturally dries out nasal passages and throat tissue, leading to discomfort, congestion, and even nosebleeds. Integrated humidification systems add moisture to the air before it reaches your airways, creating a more natural breathing experience.
Users who wake with a parched throat or stuffy nose typically benefit from adjustable humidification settings. These allow customisation based on personal comfort levels and environmental factors like bedroom humidity or seasonal changes. Some machines offer climate control technology that automatically adjusts moisture output throughout the night.
How Heated Tubing Enhances the CPAP Experience
Heated tubing works in tandem with humidification to maintain optimal moisture levels from the machine to your mask. Without heating, warm humidified air cools as it travels through standard tubing, causing water vapour to condense into droplets. This “rainout” creates an uncomfortable gurgling sensation and can wake users when cold water reaches the mask.
The heating element runs along the tube’s length, keeping air at a consistent temperature that prevents condensation. This feature proves particularly valuable for users who:
- Sleep in cooler bedrooms
- Require higher humidity settings
- Experience frequent rainout with standard tubing
- Use longer tube lengths
Understanding the Ramp Feature’s Gradual Pressure Adjustment
The ramp feature addresses a fundamental challenge: falling asleep whilst air pressure blows into your airways feels unnatural. This function starts therapy at a lower, more tolerable pressure and gradually increases to the prescribed therapeutic level over a set timeframe—typically 5 to 45 minutes.
How Does Mask Compatibility Affect CPAP Machine Choice?
Mask compatibility directly determines whether your CPAP therapy succeeds or fails. The interface between your face and the machine creates the seal that delivers pressurised air, making the mask-machine pairing as critical as the device itself.
What Makes Nasal Pillows Different from Other Mask Types?
Nasal pillows insert directly into the nostrils using soft silicone cushions. These minimalist interfaces work best for users requiring low to moderate pressure settings, typically below 12 cm H₂O. People with facial hair often prefer nasal pillows because they avoid the upper lip and chin areas where beards interfere with traditional mask seals.
The lightweight design appeals to active sleepers who change positions frequently throughout the night. Users who feel claustrophobic with larger masks find nasal pillows less restrictive. However, higher pressure requirements can cause nostril discomfort or irritation, limiting their suitability for severe sleep apnoea cases.
When Should You Choose Nasal Masks?
Nasal masks cover the entire nose whilst leaving the mouth exposed. This design accommodates a wider pressure range than nasal pillows, making them suitable for moderate to high-pressure therapy. The broader contact surface distributes pressure more evenly across the nose bridge and cheeks.
Nasal masks require consistent nasal breathing during sleep. Mouth breathers experience air leaks that compromise therapy effectiveness and cause dry mouth. The cushion design varies between manufacturers, with some offering memory foam alternatives to traditional silicone for enhanced comfort. Users with narrow nasal passages or deviated septums may struggle to achieve proper seal integrity with certain nasal mask models.
Why Do Some Users Need Full-Face Masks?
Full-face masks enclose both the nose and mouth, creating a complete seal around the lower face. These masks become essential for mouth breathers or individuals with chronic nasal congestion. Higher pressure settings above 15 cm H₂O often necessitate full-face designs to maintain adequate seal integrity.
See Also : The Future of Breathing: Why You Need an Oxygen Concentrator
What Role Does User Interface Play in Selecting a CPAP Machine?
A well-designed user interface makes the difference between a CPAP machine you’ll use consistently and one that sits gathering dust. The interface serves as your primary point of interaction with the device, particularly during those groggy nighttime moments when you need to adjust settings or troubleshoot issues.
Why Easy-to-Use Controls Matter for CPAP Success
Easy-to-use controls become essential when you’re fumbling with your device at 2 AM. Modern CPAP machines feature illuminated displays with large, clearly labelled buttons that remain visible in low-light conditions. The menu structure should feel intuitive, allowing you to navigate between settings without consulting the manual each time.
Consider these key interface elements:
- Backlit displays that adjust brightness automatically based on ambient light
- Single-button operations for common tasks like starting or stopping therapy
- Clear icons and symbols that transcend language barriers
- Tactile feedback through button design that confirms your selections
Machines with touchscreen capabilities offer visual clarity but may prove challenging for users with limited dexterity or those wearing reading glasses at night. Traditional button-based systems often provide more reliable operation when you’re half-asleep.
How Wireless Connectivity Transforms CPAP Therapy Management
Wireless connectivity has revolutionised how users and healthcare providers approach CPAP therapy. Modern machines transmit usage data automatically to cloud-based platforms, eliminating the need for manual data downloads during clinic visits.
This technology enables:
- Real-time therapy monitoring by sleep specialists who can identify issues before they derail treatment
- Mobile app integration that provides daily feedback on your sleep quality and mask seal
- Automatic compliance reporting to insurance providers without requiring manual intervention
- Remote troubleshooting that resolves problems without scheduling appointments
Apps like myAir deliver personalised coaching based on your nightly data, showing metrics such as mask seal quality, events per hour, and total usage time. These insights help you understand what affects your therapy quality, from sleeping position to mask adjustments.
Balancing Simplicity with Advanced Features
The best CPAP interfaces hide complexity behind simplicity. Basic users access essential functions effortlessly while advanced users explore deeper settings when needed.
Are There Special CPAP Models Designed for Specific Needs?
Yes, manufacturers now produce CPAP machines specifically designed for distinct user groups and lifestyles. These specialised models address unique physiological characteristics and practical requirements that standard devices may not fully accommodate.
Women’s CPAP Machines
Women’s CPAP machines recognise that female anatomy differs significantly from male anatomy in ways that affect therapy comfort. These devices typically feature:
- Lower starting pressure ranges that align with women’s generally lower pressure requirements
- Smaller, lighter masks engineered for narrower facial structures and smaller nasal passages
- Pressure algorithms calibrated to respond to female breathing patterns, which often differ in depth and frequency
- Quieter operation settings that many women prefer for their sleeping environment
The ResMed AirSense 10 AutoSet for Her exemplifies this category, using a specialised algorithm that responds more sensitively to flow limitations and partial obstructions common in female patients. This targeted approach reduces the likelihood of pressure overshooting, which can cause discomfort and therapy abandonment.
Women with smaller facial features often struggle with standard masks that create gaps or require over-tightening, leading to skin irritation and air leaks. Purpose-built women’s models pair with appropriately sized mask options that maintain proper seal integrity without excessive strap tension.
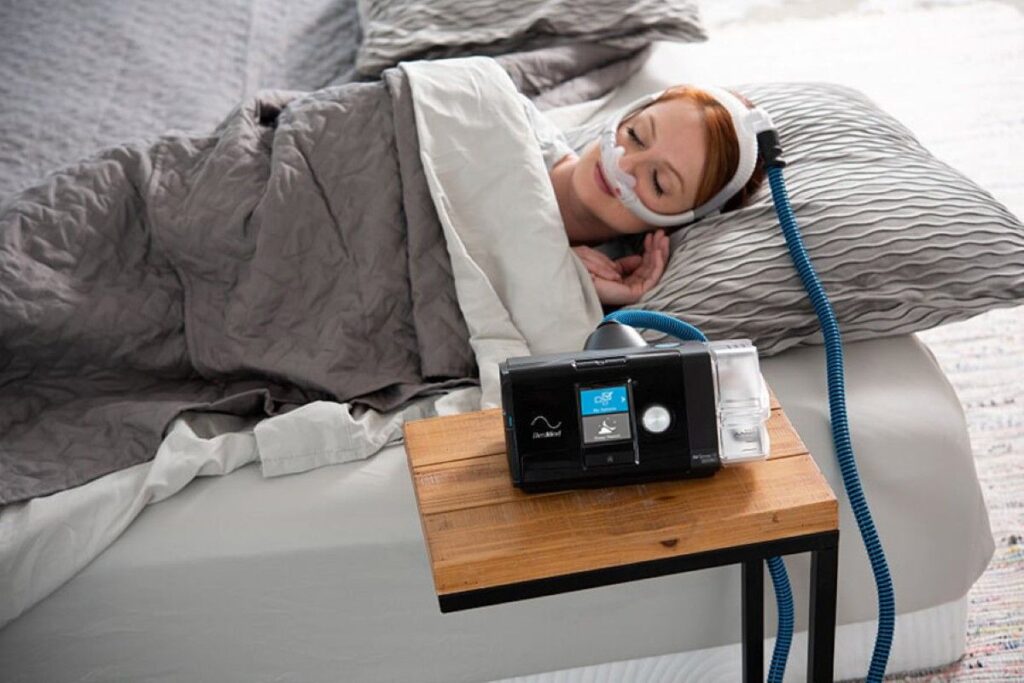

Travel CPAP Machines
Travel CPAP machines solve the challenge of maintaining therapy whilst away from home. These compact devices deliver full therapeutic effectiveness in packages roughly the size of a paperback book.
Key features include:
- Weight reduction to 300-400 grams compared to 1-2 kilograms for standard units
- Universal power adaptors compatible with 100-240V outlets worldwide
- Battery capability for camping, flights, or locations without reliable electricity
- Waterless humidification systems that eliminate the need for distilled water
- Carry cases designed to meet airline hand luggage requirements
The Transcend and Z2 Auto represent popular travel options, offering auto-adjusting pressure technology in remarkably small footprints. These machines don’t sacrifice therapeutic capability for portability—they deliver the same pressure ranges and treatment algorithms as full-sized counterparts.
How Can Users Adapt to Using Their CPAP Machine Effectively?
The adaptation period typically requires patience and a structured approach. Most new CPAP users need between two to four weeks to adjust to sleeping with their device, though individual experiences vary significantly.
Starting Small: The Gradual Introduction Method
Begin by wearing your CPAP mask during relaxed, wakeful activities. Sit on the sofa whilst watching television or reading for 15-20 minutes with the mask on but the machine off. This familiarises you with the sensation of wearing the mask without the added pressure.
Progress to wearing the mask with the machine running during these daytime sessions. Once comfortable, advance to using the device during brief afternoon naps. These shorter sessions build confidence and allow your body to adjust without the pressure of needing a full night’s sleep.
Daytime practice sessions offer several advantages:
- Lower stress levels compared to nighttime use
- Ability to remove the mask immediately if uncomfortable
- Opportunity to experiment with different positions
- Time to adjust settings without sleep deprivation concerns
The Critical Role of Professional Fitting
Proper mask fitting determines therapy success more than any other factor. A poorly fitted mask causes air leaks, skin irritation, pressure sores, and inadequate treatment—all leading to therapy abandonment.
Schedule a fitting appointment with a qualified sleep technician or respiratory therapist. These professionals assess facial structure, sleeping position preferences, and breathing patterns to recommend appropriate mask styles. They adjust headgear tension, cushion size, and positioning to create an effective seal without excessive tightness.
Return for follow-up fittings after the first week and again at one month. Facial contours change slightly with weight fluctuations, and initial swelling from mask pressure subsides within days. These adjustments ensure continued comfort throughout The Definitive Guide to Choosing the Right CPAP Machines journey.
Addressing Common Adaptation Challenges
Claustrophobia affects approximately 25% of new CPAP users. Combat this by practising relaxation techniques whilst wearing the mask, such as deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation. Some users find success by wearing just the mask frame initially, then adding cushions once comfortable.
Pressure intolerance often resolves through the ramp feature.
What Are The Risks Of Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnoea?
Untreated OSA risks extend far beyond poor sleep quality, creating serious threats to both physical health and daily functioning. When breathing repeatedly stops during sleep, the body experiences oxygen deprivation and stress responses that accumulate over time, triggering a cascade of health complications.
Immediate Daily Impact
Excessive daytime sleepiness represents one of the most noticeable consequences of untreated sleep apnoea. The constant sleep disruptions prevent the brain from completing restorative sleep cycles, leaving individuals perpetually exhausted regardless of how many hours they spend in bed.
This chronic fatigue directly impairs cognitive function. Memory consolidation suffers, concentration wavers, and decision-making abilities decline. Simple tasks become challenging, work performance drops, and the risk of workplace accidents increases substantially.
The danger extends to driving and operating machinery. Studies show that people with untreated OSA are up to five times more likely to be involved in motor vehicle accidents compared to those without the condition. Microsleeps—brief episodes of unintentional sleep lasting just seconds—can occur without warning, creating potentially fatal situations.
Cardiovascular Complications
The heart bears a significant burden from untreated sleep apnoea. Each breathing pause triggers a stress response that elevates blood pressure and forces the cardiovascular system to work harder. Night after night, this pattern strains the heart muscle and blood vessels.
High blood pressure develops in approximately 50% of people with OSA. The condition creates a vicious cycle: OSA raises blood pressure, whilst elevated blood pressure makes OSA symptoms worse. This relationship persists even in individuals taking blood pressure medications.
Heart rhythm disturbances become increasingly common. Atrial fibrillation, the most prevalent type of arrhythmia, occurs at significantly higher rates in those with untreated OSA. The irregular heartbeat can lead to blood clots, stroke, and heart failure if left unaddressed.
The risk of heart failure doubles in individuals with moderate to severe untreated OSA. The heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently deteriorates under constant strain, potentially leading to fluid accumulation in the lungs and extremities.
Stroke Risk
Stroke represents one of the most severe unintended consequences of untreated obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA). The intricate relationship between OSA and stroke risk is primarily attributed to two factors: cardiovascular complications and disrupted sleep architecture.
People with untreated OSA face a significantly higher likelihood of experiencing strokes compared to those without the condition. Research indicates that individuals suffering from moderate to severe OSA have an approximately 2-4 times greater risk of stroke than their non-apnoeic counterparts.
The underlying mechanisms behind this heightened risk involve both direct and indirect pathways:
- Direct impact on vascular health: Repeated episodes of oxygen deprivation during apnoeic events contribute to inflammation within blood vessels, promoting atherosclerosis—the buildup of fatty plaques that narrow arteries over time.
- Indirect influence through hypertension: As discussed earlier, untreated OSA often leads to high blood pressure (hypertension), which is a well-established risk factor for stroke development.
By addressing these interconnected factors through effective treatment strategies—such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy or lifestyle modifications—it becomes possible not only to mitigate symptoms but also reduce long-term cardiovascular risks associated with obstructive sleep apnoea.
How Does Effective CPAP Use Improve Health Outcomes?
Consistent CPAP therapy transforms sleep quality by keeping airways open throughout the night, allowing users to experience complete, uninterrupted sleep cycles. This restoration of natural sleep patterns enables the body to go through all essential sleep stages, including deep restorative sleep and REM sleep, which are often disrupted in untreated OSA patients.
Improved Sleep Quality
Users usually notice a significant reduction in loud snoring within the first few nights of therapy, creating a quieter sleep environment for both themselves and their bed partners. The frequent awakenings that characterise OSA—often occurring dozens of times per hour—virtually disappear as the continuous positive airway pressure prevents airway collapse.
Cardiovascular Benefits
The cardiovascular system experiences immediate relief from CPAP therapy. Blood pressure readings often normalise within weeks of starting treatment, as the body no longer endures repeated oxygen desaturation events throughout the night. The heart rate stabilises, reducing the strain caused by the body’s panic response to breathing cessation. Studies show that regular CPAP users have measurably lower risks of developing irregular heartbeats, heart failure, and stroke compared to those who remain untreated.
Daytime Functioning Improvements
Daytime functioning improves significantly with proper CPAP adherence. Users report:
- Enhanced mental clarity and concentration
- Improved memory retention and recall
- Increased energy levels throughout the day
- Better mood regulation and reduced irritability
- Decreased reliance on caffeine or stimulants
The cognitive benefits go beyond simple alertness. Research indicates that sustained CPAP therapy can reverse some of the brain changes associated with chronic sleep deprivation, including improvements in executive function, decision-making abilities, and reaction times. This cognitive restoration greatly reduces the risk of workplace accidents and motor vehicle collisions.
Metabolic Health Response
Effective CPAP use also has a positive impact on metabolic health. The body’s insulin sensitivity improves, making blood sugar regulation easier for those with diabetes or prediabetes. Weight management becomes more achievable as energy levels increase and hormonal imbalances that promote weight gain begin to correct themselves.
Long-term adherence to CPAP therapy—defined as using the device for at least four hours per night on 70% of nights—correlates with the most significant improvements in these health outcomes.
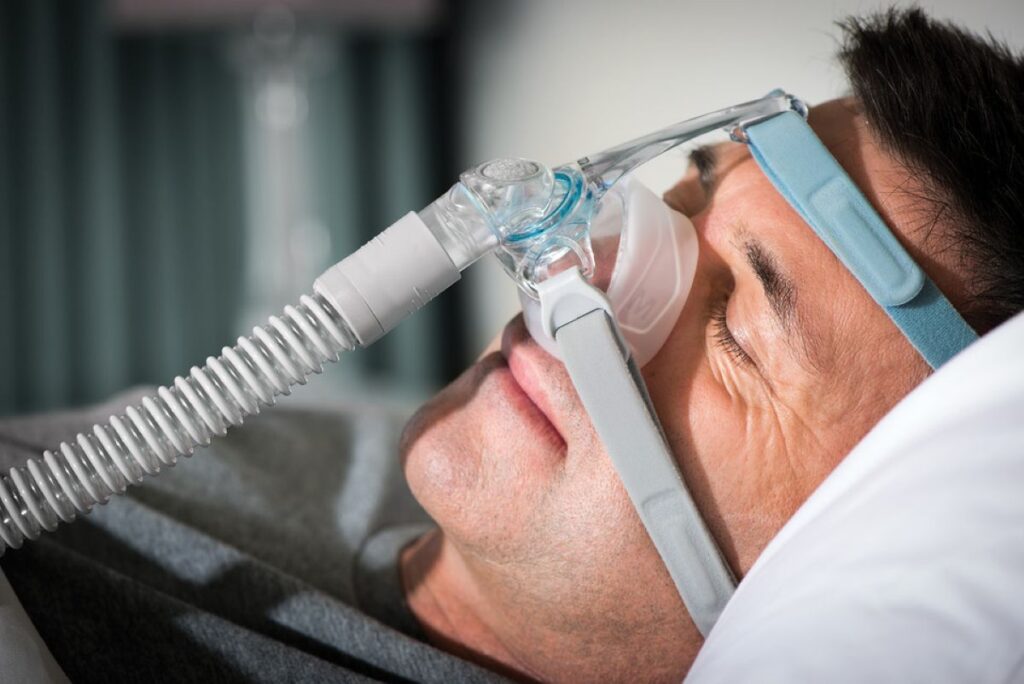
What Additional Considerations Should Users Keep in Mind When Choosing a CPAP Machine?
Managing side effects is an important factor when choosing your CPAP device. Many users feel uncomfortable temporarily during the first adjustment period, but knowing these challenges in advance helps you pick a machine designed to handle them.
What Side Effects Might New CPAP Users Experience?
Dry mouth is one of the most common complaints during early CPAP therapy. This happens when air escapes through an open mouth or when humidity levels are not enough. Some people may also experience nasal congestion, skin irritation from mask contact, and aerophagia (swallowing air) during their first few weeks of treatment.
How Can Humidification Settings Address Dryness Issues?
Built-in humidifiers directly tackle dryness concerns. Start with mid-range humidity settings and adjust gradually based on your comfort level. Heated tubing maintains consistent moisture delivery, preventing condensation while ensuring optimal hydration throughout the night.
Practical humidification tips:
- Increase humidity levels gradually if you wake with a dry throat
- Use distilled water to prevent mineral build-up in the humidifier chamber
- Clean the water chamber daily to maintain hygiene and optimal function
- Consider a chin strap if mouth breathing causes persistent dryness
What Should Users Do About Nasal Congestion?
Nasal congestion often improves within 2-3 weeks as your body adjusts. Saline nasal sprays before bedtime can provide immediate relief. If congestion persists beyond the adjustment period, consult your healthcare provider about adjusting pressure settings or exploring different mask styles that reduce nasal airflow resistance.
How Can Mask-Related Discomfort Be Minimized?
Skin irritation usually comes from improper mask fit or over-tightening. Your chosen CPAP machine should accommodate multiple mask options, allowing you to switch styles if irritation continues. Mask liners create a protective barrier between skin and silicone, while proper cleaning routines prevent bacterial build-up that worsens sensitivity.
When Should Users Consider Alternative Treatment Modalities?
Some individuals cannot tolerate CPAP therapy due to persistent discomfort or specific medical conditions such as claustrophobia. In such cases, it’s essential to discuss alternative treatment options with your healthcare provider. These may include oral appliances, positional therapy, or even surgical interventions depending on the severity of your sleep apnoea.
Always remember that finding the right solution may take time and patience. It’s crucial not only to focus on immediate relief but also to prioritise long-term health benefits associated with effective sleep apnoea management.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What are CPAP machines and how do they effectively treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)?
CPAP machines deliver continuous positive airway pressure to keep the airways open during sleep, effectively treating obstructive sleep apnea by preventing airway collapse. Choosing the right CPAP machine is crucial for effective therapy and patient comfort.
What are the different types of CPAP machines available and how do they differ?
There are fixed pressure CPAP machines that provide constant air pressure, and auto-adjusting CPAP machines that modify pressure based on breathing patterns and apnea severity. Each type offers unique benefits and limitations depending on individual needs.
Which comfort features should users look for when selecting a CPAP machine?
Key comfort features include built-in humidification to reduce dryness, heated tubing to maintain consistent humidity levels, a ramp feature that gradually increases pressure to ease users into sleep, and quiet operation to ensure undisturbed rest for both users and their partners.
How does mask compatibility influence the choice of a CPAP machine?
Different mask types such as nasal pillows, nasal masks, and full-face masks suit various user preferences and needs. Ensuring compatibility between the mask type and CPAP machine affects overall comfort, seal integrity, and the effectiveness of therapy.
What role does the user interface play in selecting a CPAP machine?
A user-friendly interface with easy-to-use controls facilitates seamless operation, especially during nighttime use. Wireless connectivity features enable data transfer to healthcare providers or mobile apps for remote monitoring and enhanced support.
Are there specialised CPAP models designed for specific user needs?
Yes, there are women’s CPAP machines tailored to smaller face sizes or narrower nasal passages for improved fit and comfort. Additionally, travel CPAP machines offer compact designs with lightweight builds and battery options for convenient on-the-go therapy without compromising treatment efficacy.

